While Bitcoin was designed to facilitate secure money transfers, Ethereum was designed to enable developers to create decentralized applications (dApps).
Most of the new Layer 1 protocols feature advancements far beyond Bitcoin’s basic functionalities.
Qtum incorporates some of the best features of both Ethereum and Bitcoin. The protocol stands out due to its unique design and innovative fusion of key elements from the two most popular blockchains.
Qtum’s goal is to be a hybrid blockchain platform that combines the security of Bitcoin with the features of Ethereum in an efficient and low-cost manner.
This article thoroughly examines the Qtum Network’s distinguishing features.
What is Qtum?
Qtum is a public, open-source blockchain network that relies on a decentralized and secure Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism. It is based on the same transaction model as Bitcoin, with the added functionality of smart contracts.
The project has several tools for developing decentralized apps and a wallet ecosystem that supports multiple cryptocurrencies.
The Qtum team has worked closely with researchers from top universities, drawing on the expertise of an open-source global talent pool. Qtum’s applications are built to connect the blockchain to the real world.
The project’s goal is to meet the needs of businesses by creating a business-friendly development environment and blockchain solutions for enterprise customers.
QTUM, the blockchain’s native token, is used to pay for smart contract execution. The token can also be staked to contribute to network security and be used to participate in platform governance.
Qtum’s QRC-20 token standard can be used by businesses and programmers alike. This token standard can also be used in decentralized applications. QTUM gas fees are required for all QRC-20 trades.
Qtum: The Background
Qtum has joined the ranks of the relatively few networks that have thrived since its initial launch in September 2017. Qtum was created to create a better smart contract platform by combining the best parts of the two most popular blockchains to create something entirely new.
The result was a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) smart contract platform based on unspent transaction outputs (UTXOs). This allows for a more secure system that is easier to use and does not necessitate as much user validation work.
Since Qtum is based on the Bitcoin codebase and was created by forking it, many of Bitcoin’s original goals and features are preserved in the Qtum ecosystem. Qtum’s main takeaway from Bitcoin was how it handles unused tokens.
Qtum accumulates tokens left over from various transactions in a user’s wallet and then selects a node to validate them based on the coinage of each node. As a result, the network’s security improves significantly, making it easy for users to mine new tokens.
Bitcoin has proven to be far more secure than almost any other distributed ledger network. However, it still has significant drawbacks that developers must address to improve the user experience.
Bitcoin’s validation process is based on a Proof-of-Work (PoW) algorithm, which necessitates the use of complex computing hardware and a substantial amount of energy.
Many users would like to participate in the validation process but lack the required resources or knowledge. Qtum introduces a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mining algorithm to help with the process and improve the user experience.
How Does Qtum Work?
The Qtum team modified Bitcoin’s code so that its users could build Ethereum-like smart contract applications on top of it.
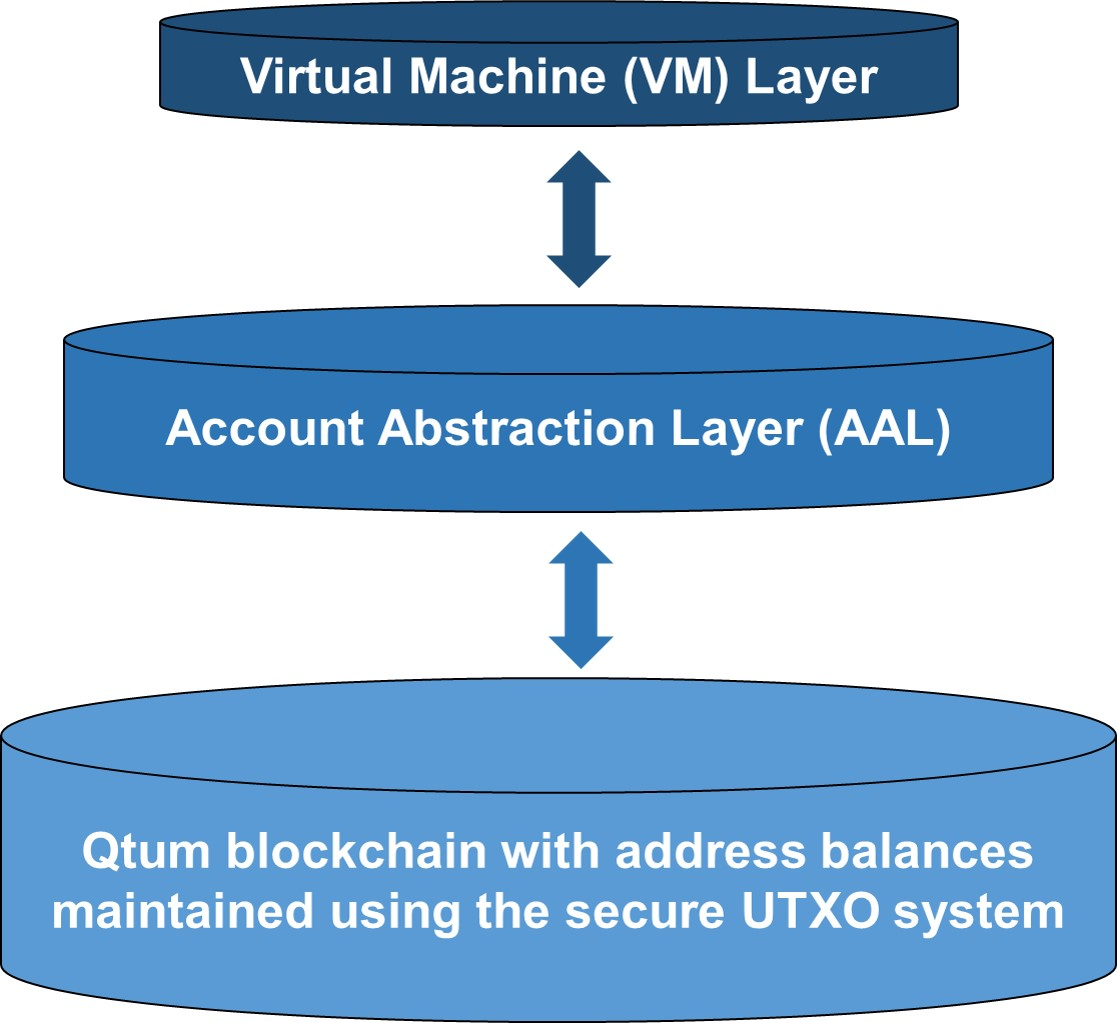
In a nutshell, Qtum’s base layer copies the transaction model of Bitcoin (i.e., UTXO). An additional layer (located on top) operates in a way that is similar to Ethereum’s virtual machine (EVM) to execute decentralized programs and its smart contracts.
Qtum, like Ethereum, has a virtual machine that can be used to create and run code across its decentralized network of computers.
Account Abstraction Layer
Qtum’s signature technology, the Account Abstraction Layer (i.e., AAL), makes it possible for the Qtum blockchain to communicate between the two layers. The AAL paves the way for smart contracts with functionality similar to that of Ethereum through the addition of a few new commands to Bitcoin’s core code.
Finally, after processing smart contract transactions, the AAL appends new blocks to the blockchain ledger.
Mutualized Proof-of-Stake
This is a type of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus that Qtum employs to keep its network in sync. To validate and process transactions on the network, nodes must stake QTUM in a wallet.
These nodes are compensated for their efforts by receiving a percentage of transaction fees, which are paid in QTUM and newly created QTUM in each block.
Each new block’s reward is distributed evenly among the nodes that generated it and the nine nodes that came before it. The project claims that hiding the immediate block reward amount will reduce the likelihood of attacks.
Unique Features of Qtum
Qtum was the first blockchain to implement the UTXO transaction model and smart contract capabilities. The project hopes to strike a balance between Bitcoin’s security and Ethereum’s functionality by employing the more time- and resource-efficient Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism.
Because of how the technologies underlying the Decentralized Governance Protocol and the Account Abstraction Layer were implemented, this pragmatic design approach outshines other blockchains in terms of performance.
Qtum disregarded the Bitcoin blockchain’s reliance on transaction size alone to calculate the mining fee. Since Ethereum’s gas model permits the return of unused gas following a transaction, it was adopted for use in this project.
Qtum, on the other hand, intends for its gas fees to be much lower than Ethereum’s and employs a market-based fee structure that benefits both users and miners.
Quantum Token and Ecosystem
QTUM is the network’s native utility token, and it is used to carry out transactions. Although QTUM’s price peaked in early 2018, it has done relatively well since then due to its real-world utility.
Although Qtum is not as well-known as some of its rival smart contract platforms, it does provide a home for a diverse set of decentralized applications. The team is also constantly brainstorming ways to entice programmers to create for the Qtum platform.
Qtum is compatible with various dApps, such as the encrypted messaging service Beechat, the social media platform Qbao, the copyright tracking platform and video exchange Vevue, the prediction market Bodhi, and many more. The most popular app that runs on the Qtum blockchain is Pundi X, a crypto project that functions as a point-of-sale system.
Qtum Tokenomics
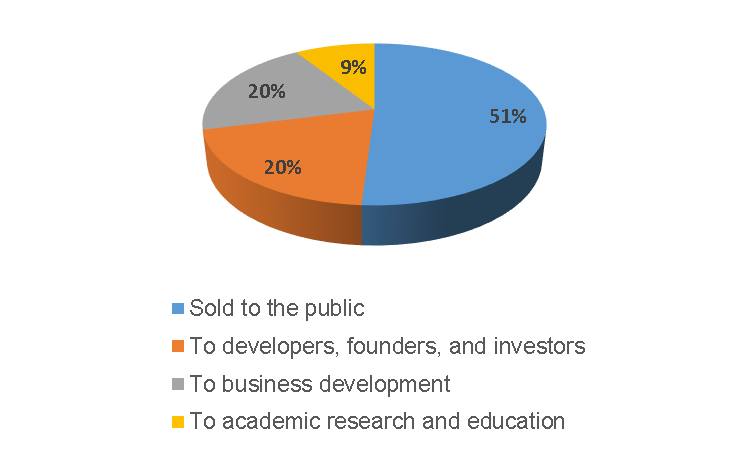
In March 2017, Qtum conducted an initial coin offering (ICO), distributing 100 million QTUM to the public. From this amount, 51% was sold to the public, 20% went to the project’s creators and early backers, 20% went toward expanding the company’s operations, and 9% was set aside for research and education.
More QTUM tokens have been created as incentives for validating blocks on the network, adding to the original 100 million tokens. The minimum block reward has been reduced from 4 QTUM to 2 QTUM every four years since its inception.
According to the schedule for awarding blocks on the chain, block rewards will cease to be distributed sometime around 2045. When that happens, the 107,822,406 QTUM coins in circulation will be the maximum that can be created.
How to Buy QTUM
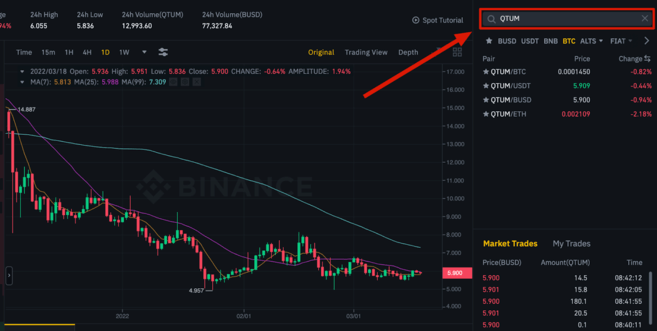
This section explains how to purchase QTUM on Binance.
There are two ways to buy QTUM on Binance. QTUM can be purchased using major credit and debit cards in various fiat currencies. To purchase QTUM, head to Binance’s [Buy Crypto with Debit or Credit Card] page, select your preferred payment method, and then enter QTUM in the lower field.
The next step is to confirm the details of your purchase by clicking [Continue] and following the on-screen instructions.

QTUM can also be purchased with Bitcoin USD, Bitcoin, or Ethereum. To find QTUM trading on Binance, go to the exchange page and enter QTUM in the search bar for trading pairs. This will display a list of all currency pairs that can be traded.
In Conclusion,
- Qtum’s decentralized governance protocol platform, which allows for seamless blockchain modification, and its abstraction layer, which enables users to use Ethereum’s smart contracts via the Bitcoin blockchain, are both firsts in the blockchain industry.
- These innovations make it easier than ever for businesses and even individuals to reap the benefits of blockchain systems. As long as the project keeps its pioneering spirit in a rapidly evolving blockchain world, it has everything it needs to succeed.
- Qtum aims to be the most secure and functional cryptocurrency network by fusing Bitcoin’s UTXO transaction model with Ethereum’s virtual machine. Qtum is highly effective because it incorporates a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which addresses the shortcomings of competing platforms.
Disclaimer: This article is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be considered trading or investment advice. Nothing herein should be construed as financial, legal, or tax advice. Trading or investing in cryptocurrencies carries a considerable risk of financial loss. Always conduct due diligence.
If you would like to read more articles like this, visit DeFi Planet and follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram.
“Take control of your crypto portfolio with MARKETS PRO, DeFi Planet’s suite of analytics tools.”





















