Blockchain technology is revolutionizing several sectors through the introduction of decentralized finance, secure transactions, and other remarkable innovations. Blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) are disrupting almost every industry, from finance to healthcare, energy, telecommunications, and supply chains.
However, many people confuse distributed ledger technology with blockchain. The term “blockchain” (not blockchain technology) refers to a type of distributed ledger. It is critical to note that distributed ledger technology, such as blockchain, has a wide range of applications.
This article comprehensively examines the top use cases of distributed ledger technology across various sectors.
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
DLT is the technological framework and protocol that enables concurrent access, verification, and modification of the records that define distributed ledgers. It operates via a computer network that connects multiple organizations or locations. DLT employs cryptography to encrypt data and restrict access to those who are authorized to see it. This is accomplished through the use of cryptographic signatures and keys.
Furthermore, the technology creates a database that cannot be altered. This means that saved information cannot be deleted, and any changes are permanently recorded for posterity. DLT represents a significant shift in how information is received and transmitted.
This is because it moves record-keeping away from a single, authoritative location and into a decentralized system where all relevant entities can read and amend the ledger.
As a result, all other entities can see who is accessing and changing the ledger. Because DLT is open, there is a high level of trust, making it nearly impossible for fraud to occur in the ledger. As a result, DLT eliminates the need for a third-party provider while also protecting the ledger from manipulation or central authority.
Why is DLT Important?
Distributed ledger technology can significantly improve record-keeping by altering some principles governing how businesses gather and share the data that goes into their ledgers.
To understand this, think about paper or old-school electronic ledgers where all changes have to go through a single point of control. To maintain centralized control in such a system, firms must invest significant labour and processing power. Furthermore, centrally-controlled ledgers are often not always up to date or accurate.
Every entity that supplies data to the ledger has the potential to be a source of fraud or inaccuracy, making the process vulnerable to errors and manipulation. Also, no party adding information to the central ledger can effectively check the accuracy of the information coming from the other participants.
Distributed ledger technology, on the other hand, allows for real-time sharing. This technology ensures that the ledger is always up to date. It also promotes transparency because every participating node can view any changes made to the ledger. It is inherently safer because there is no single point of failure or target for hackers.
Because there is no need for a central authority or middleman, distributed ledger technology has the potential to accelerate transactions and significantly reduce transaction costs.
Components of a DLT Network
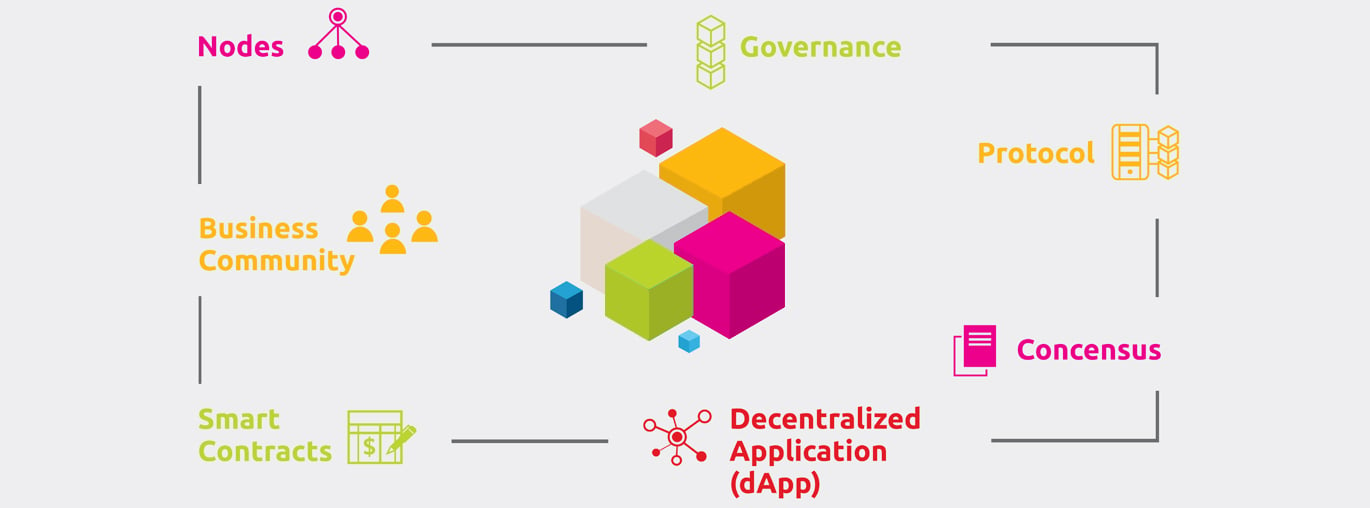
Business Community
This refers to a group of individuals or organizations with shared objectives.
Nodes
Nodes are devices that are connected to a network.
Consensus
This is a widely used method of authorizing transactions and sharing data.
Protocol
A protocol is a specific set of software guidelines that govern how a community communicates with a network.
Governance
This is the system for making decisions within the company’s network.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing programs that control and secure network transactions.
Decentralized Application (dApp)
A dApp is a network interface that allows interaction between the community and the business community on a DLT network.
Is DLT the Same as Blockchain?
Despite the frequent conflation of the two terms, not all DLTs are blockchains. All blockchains, however, are DLTs. Distributed ledger technology consists of a distributed database of records that must be validated at each node before modifications to the ledger can be made.
The transactional architecture of various blockchains differs. The fundamental point to remember is that blockchain implementations group verified transactions into time-stamped, cryptographically hashed blocks, with each new block’s hash referring to the previous block’s hash to form a chain.
Unlike a DLT, the blockchain ledger is globally accessible to all network participants, and any changes to it are immutable, just like a regular DLT. The ledger’s transactions are only accessible to the parties who are listed on it. A DLT may only be a distributed system of records (SoR), whereas a blockchain typically employs a cryptocurrency to facilitate financial transactions.
Use Cases of DLT
The Use of Blockchain Authentication to Prevent Identity Theft
The rapid expansion of the internet has resulted in the emergence of an industry devoted to stealing and using personally identifiable information (PII) to access online services.
According to the data obtained from the Breach Level Index, 2.6 billion records were stolen, lost, or made public around the world in 2017 (an increase of 88% from what was obtained in 2016).
It is unlikely that the internet’s growth and all the services it connects to will subside. Because more businesses are implementing Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, personal information is more vulnerable than ever.
A blockchain’s immutability can provide a higher level of inherent security for personal identity. According to a Forbes article, Civic’s Secure Identity Platform (SIP) was used as an example of a distributed platform for conducting secure transactions with PII that has been cryptographically encrypted.
Customers can use services such as SIP to perform security checks to authenticate and encrypt personal information. As a result, businesses such as banks and retail merchants can use a person’s digital profile to confirm the legitimacy of transactions.
The Use of Smart Contracts in Enhancing Industrial Processes
It is worth noting that smart contracts are one of the most well-known applications of DLTs in the industrial sector.
The term “contract” makes perfect sense, given that the code lays out explicit requirements and guidelines for carrying out a specific set of predetermined actions and behaviors. It’s interesting to note that the basic structure of smart contracts makes them suitable for a wide range of applications where they can help define all aspects of a partnership.
Smart contracts that use distributed ledger technology and blockchain may garner a lot of attention in the near future. The following are some major advantages of using smart contracts:
- Smart contracts provide a technique for guaranteeing greater transaction transparency. The fact that smart contracts can be used on a public blockchain network may help to increase transparency.
- Smart contracts provide protection against fraud due to their immutable blockchain record.
- They provide significant cost savings. Smart contracts can significantly reduce the amount of time required to manage various activities and procedures.
- Speed is another important feature of distributed ledger technology applications.
- Smart contracts make it easier to circumvent traditional approval procedures. This means that distributed ledger technologies can help eliminate the need for traditional intermediaries in transactions.
Global Payments
A blockchain is a highly encrypted database shared across thousands of machines, with each entry validated and encrypted. The resulting uniformity and openness greatly benefit banking transactions. Encryption protects the data, and mutual verification protects it internally and externally to prevent errors.
The idea is to handle foreign payments using DLT without the need for an intermediary such as a bank, lowering transaction costs while also speeding up transactions. Banks are also utilizing DLT to replace time-consuming and inefficient manual international transactions with a more user-friendly and efficient system.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Data security is a major issue in the IoT space. DLT provides a secure means of communicating large amounts of data, which often includes personal information. Several projects are also attempting to integrate DLT and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
Other applications of DLT in the IoT space include:
Machine and Plant Monitoring
Sensors, rather than cloud technology, can be used to monitor the operation of machines and plants.
Supply Chain Management
Sensors are used in supply chain management to track the location and condition of each item and container.
Healthcare
Intelligent sensors can record, transmit, and store bio-data about individuals, while DLT can help secure them.
In Conclusion
- These are just a few examples of the sectors that DLT could disrupt in the near future. One of the most important characteristics of a distributed network is its versatility.
- The applications of distributed ledger technologies benefit institutions while also providing users with exclusivity and control.
- For example, faster transaction processing may improve the effectiveness of financial institutions.
- We are confident that new and interesting DLT applications will emerge in the Internet of Things and other related fields.
If you would like to read more articles like this, visit DeFi Planet and follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram.
“Take control of your crypto portfolio with MARKETS PRO, DeFi Planet’s suite of analytics tools.”





















