Last updated on September 3rd, 2025 at 04:05 am
Ethereum spawned from the intention to address the limitations of the Bitcoin blockchain. Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum introduced support for smart contracts, enabling its use in decentralized finance (DeFi) and the creation of various decentralized applications (dApps). However, Ethereum itself has faced challenges in meeting the expanding requirements of its ecosystem.
With a significant number of developers and a wide array of dApps, the Ethereum blockchain demands a network capable of handling this increasing workload. To address these demands, the Ethereum Foundation and co-founders like Vitalik Buterin proposed a series of upgrades to enhance the Ethereum blockchain. These upgrades are implemented in a decentralized manner, allowing the Ethereum community to actively contribute to their development and implementation.
Ethereum 2.0, the latest upgrade of the Ethereum blockchain, represents the ongoing phase of Ethereum’s development. It was introduced to tackle the existing challenges in the Ethereum ecosystem. The upgrade commenced with the launch of the Beacon Chain in December 2020.
What is Ethereum 2.0?

Though it is commonly referred to as Ethernet 2.0, the Ethereum Foundation has clarified that it should be called the ‘consensus layer’ and the underlying Ethereum chain, the ‘execution layer.’ This distinction highlights that the Ethereum upgrade builds on the already-existing framework of Ethereum by adding a new layer that improves the network’s capabilities rather than changing the entire network.
The Foundation’s rebranding as the ‘consensus layer’ is just to clear up the confusion about Ethereum 2.0 being a completely new chain.
Why Ethereum 2.0?
Let’s delve into some of the reasons that prompted the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade.
Scalability issues and network congestion
This is the biggest reason for the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. The slow transaction throughput of Ethereum has been a significant challenge for users and developers alike. It has rendered the network unsuitable for mass adoption as a public blockchain that can process transactions in real time.
High transaction fees and slow confirmation times
To hasten transaction processing on the Ethereum blockchain, users often have to pay high gas fees to surpass the queue of pending transactions. A notable example is a recent incident where someone paid 64 ETH as a gas fee on the Ethereum network, equivalent to a staggering $119,121 for a single transaction.
These exorbitant fees make it impractical to conduct small transactions like buying a coffee with ETH. On the other hand, choosing to wait in line for transaction confirmation on the Ethereum network could result in delays that may cause you to miss important deadlines, such as a train departure while waiting for a payment transaction to be confirmed for your ticket.
Environmental concerns and energy consumption
Similar to the Bitcoin blockchain, Ethereum initially relied on the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to validate and add new blocks to the network. However, this energy-intensive system faced significant criticism as it consumed substantial amounts of electricity, raising concerns about its environmental impact.
Consequently, the Ethereum blockchain became an unlikely candidate for widespread adoption of blockchain technology, despite its pioneering role in dApps.
Ethereum vs. Ethereum 2.0: Exploring the Key Features of Ethereum 2.0
Both Ethereum and Ethereum 2.0 share the same foundational framework. In Ethereum 2.0, Ether (ETH) is still used as the payment for gas on the Ethereum network.
The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade comprises several significant events that have taken place to enhance the Ethereum network. Here are some of these events:
Shifting to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism
One of the critical features of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade is the transition from the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus to the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus. This shift significantly reduces the energy consumption on the Ethereum network.
Miners no longer need to use extensive computational power to validate transactions and add new blocks. Instead, they are required to lock up a certain amount of Ether (ETH) as a stake to secure the network.
In the PoS consensus, the individuals responsible for securing the network are known as validators. They are selected to verify transactions based on the amount of Ether (ETH) they stake on the network.
Introduction of the Beacon Chain
The Beacon Chain is a crucial component of the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. It was initially launched in December 2020 as a testnet feature; it operated as a parallel version of the Ethereum blockchain.
One of the significant features supported by the Beacon Chain is sharding, which involves dividing transactions into different blocks on the Ethereum blockchain. This allows for simultaneous verification of separate transactions across multiple blocks, thus, increasing scalability.
However, the successful implementation of rollups, a Layer 2 scaling solution, has somewhat diminished the urgency for sharding. A combined approach of a new variation of sharding and rollups is expected to enable Ethereum to achieve a throughput of more than 100,000 transactions per second (tps).
Introduction of Staking Pools
The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade seeks to address the issue of centralization in transaction verification on the Ethereum network. Prior to the upgrade, the network exhibited a centralized tendency, with large organizations dominating the verification process due to the resource-intensive nature of the Ethereum blockchain.
To achieve decentralization, Ethereum 2.0 introduces measures that make network participation more accessible to individuals with smaller funds. Participants can either directly stake the minimum required amount of Ether (ETH) on the network or deposit their ETH into Ethereum 2.0 staking pools and delegate to other validators. This shift promotes decentralization and diminishes the influence of centralized entities.
Effects of Ethereum 2.0
The effects of Ethereum 2.0 encompass the transformations observed in the Ethereum network from the introduction of the Beacon Chain, the transition to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network, and the subsequent developments up until the present time.
Mining
To participate as a validator and validate transactions on the Ethereum network, you are required to run a full node and make a deposit of 32 ETH. While this deposit may be expensive for the average investor, it’s more affordable compared to mining on a PoW network. Additionally, the energy consumption of the PoS network is significantly reduced, up to 99.95% less than the PoW network.
If you can’t afford a 32-ETH deposit, an alternative is to stake your Ether in staking pools. By doing so, you can earn rewards in proportion to your deposits. It’s important to note that staking pools may charge a maintenance fee for their services.
Gas Fees
Although a core part of Ethereum 2.0 is to achieve scalability and reduce transaction costs, the gas fees on the Ethereum network have yet to feature a “magical decline” as initially anticipated. These fees are expected to remain so until a series of additional upgrades are completed on the Ethereum blockchain. Only recently, a user had to pay over $100,000 in gas for a single transaction.
Transaction Processing Time
Contrary to expectations, the transition to Ethereum 2.0 has not resulted in a significant decrease in transaction processing time. Despite the block time being reduced to 12 seconds from the previous 13.3 seconds in the Proof-of-Work (PoW) network, it has not had a substantial impact on faster transaction processing due to ongoing network congestion issues.
However, future network upgrades are expected to make the Ethereum network process up to 100,000 transactions per second (TPS).
Increased Block Finality
The block finality time on the Ethereum network has increased from less than 5 minutes during the Proof-of-Work (PoW) phase to approximately 15 minutes in the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) phase. This longer block finality time contributes to the enhanced security of the Ethereum blockchain compared to its previous state.
However, it is important to note that this change in block finality does not result in faster transaction processing on the network. Transaction speed remains largely unaffected, and the primary focus of the PoS transition is on improving network security rather than transaction processing times.
Liquid Staking
The transition of Ethereum from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network introduces a novel approach to securing the network and earning rewards, with liquid staking being one of the methods available. Liquid staking enables owners of Ether (ETH) to stake their tokens on the network and still have access to them, offering an alternative to traditional methods where ETH would be locked up during the staking process.
This alternative presents a user-friendly option for individuals without extensive technical expertise to participate in staking their ETH on the Ethereum blockchain.
Decentralization
In addition to running individual nodes, which currently require 32 ETH ($59,430 at the time of writing), staking offers a less energy-intensive and more cost-effective method compared to mining. Furthermore, variations of staking, such as liquid staking, have expanded the opportunity for more individuals to participate in the Ethereum network and contribute to its security. Consequently, the decentralized nature of the Ethereum blockchain has been enhanced thanks to these developments.
Green Energy
The Ethereum blockchain has made significant strides toward becoming a greener and more energy-efficient project. With the transition to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network, Ethereum has substantially reduced its electricity consumption by up to 99.95% compared to its previous Proof-of-Work (PoW) network.

This shift to PoS has positioned Ethereum as an energy-saving initiative, consuming less energy than prominent multinational companies like Netflix and YouTube. These improvements are expected to alleviate the concerns and criticisms regarding Ethereum’s energy consumption during its PoW phase.
What’s Next After Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum’s development follows a structured rollout plan consisting of predefined phases, yet it retains the flexibility to accommodate any necessary changes and prioritize critical upgrades.
In November 2022, Vitalik Buterin shared an updated roadmap outlining the expected phases for the future progression of the Ethereum network.
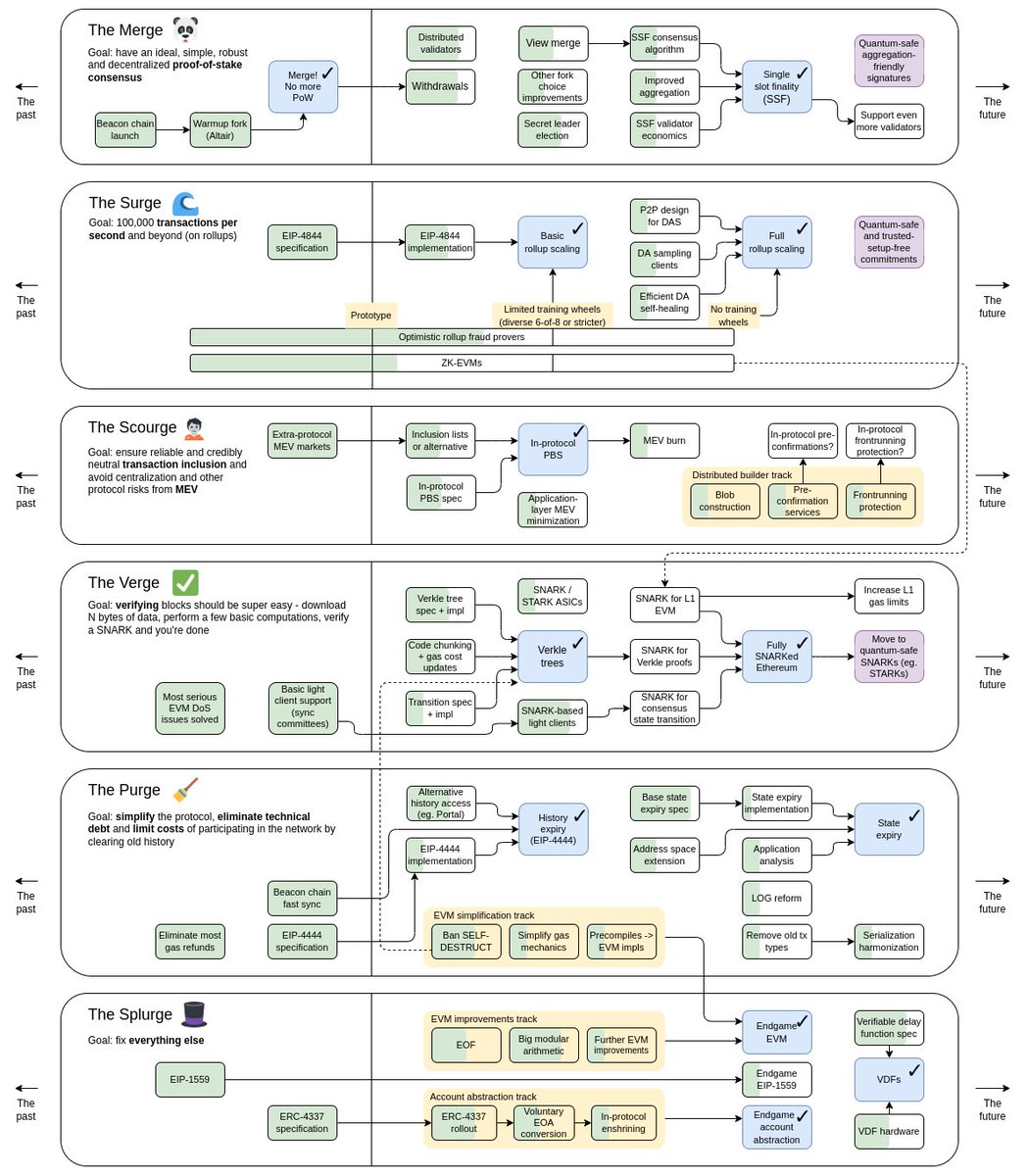
Here is what is expected to happen in each of these phases.
The Surge (Scalability Upgrades)
Ethereum 2.0 aims to enhance network scalability, but this scalability will be implemented gradually over time. In future upgrades, Ethereum will introduce features to incorporate rollups, which will significantly improve scalability and enable the processing of up to 100,000 transactions per second (tps). Moreover, Ethereum will introduce danksharding, a data sharding feature, to make rollups more cost-effective and scalable for users. The scalability upgrades that follow the release of Ethereum 2.0 are collectively referred to as ‘the Surge.’
The Scourge (Censorship resistance, decentralization, and MEV protection)
This upgrade aims to enhance the decentralization of the Ethereum network and provide better protection for users against risks like maximum Extractable Value (MEV). This upgrade, known as ‘the scourge,’ will contribute to strengthening the overall security of the Ethereum network.
The Verge (Block Verification Upgrades)
The term “the Verge” refers to a set of upgrades in the Ethereum network that aim to streamline the process of verifying blocks. These upgrades are designed to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the Ethereum network in terms of transactions per second (tps) and block finality.
As part of the Verge upgrades, Vitalik has proposed the implementation of Verkle trees, an advancement over Merkle trees. Verkle trees are expected to make block verification less resource-intensive by reducing the amount of data stored on validators’ nodes. This optimization would reduce the computational burden on validators, resulting in faster and lighter verification of blocks.

Overall, the Verge upgrades seek to significantly enhance the transaction processing capacity and block confirmation speed of the Ethereum network.
The Purge (Reduction of Computational Costs)
Even with the transition to a Proof of Stake (PoS) network, running an independent node on the Ethereum network to contribute to its security still demands a significant investment in computational power capable of handling the historical data stored on the network. However, in the upcoming phase known as ‘the Purge,’ Ethereum will no longer require nodes to store historical data. As a result, the computational requirements for running Ethereum nodes will be reduced significantly. This change will make it much easier and more cost-effective to run Ethereum nodes without incurring high computational costs.
The Splurge (Finishing Touch)
Following ‘the Splurge,’ a series of upgrades are anticipated in the Ethereum network. These upgrades are designed to validate and verify the effectiveness of the previous upgrades implemented in the network.
The purpose of these subsequent upgrades is to ensure that the earlier changes made to the Ethereum network are functioning as intended and delivering the expected outcomes. This phase aims to thoroughly assess and confirm the successful implementation of the preceding upgrades, thus maintaining the reliability and efficiency of the Ethereum network.
The implementation of all these upgrades is expected to be an extensive and time-consuming process, with some requiring concurrent or parallel execution. The realization of all upgrades will demand a considerable amount of time and energy due to their complexity and interconnectedness.
If you would like to read more articles like this, visit DeFi Planet and follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and CoinMarketCap Community.
“Take control of your crypto portfolio with MARKETS PRO, DeFi Planet’s suite of analytics tools.”





















