Last updated on March 28th, 2024 at 04:06 pm
The early success of Web3 games like Axie Infinity attracted significant media attention and a large following of gamers and enthusiasts. The concept of Play-to-Earn (P2E)—rewarding gamers for active participation—sharply contrasts with traditional gaming systems. In traditional gaming spaces, players invest time and cannot directly generate profits as they do with these Web3 games.
However, like any new concept, Web3 gaming must overcome numerous obstacles and challenges to establish its worth and pass the test of time. Security has emerged as a major concern, given the frequent hacking and vulnerability exploits in the Web3 space making headlines.
For example, In April 2023, Tales of Elleria, a Web3 game project, fell victim to an Arbitrum Bridge hack, leading to the theft of 140 ETH, worth approximately $273,000. The hacker distributed the stolen funds across four transactions, exploiting a vulnerability in the smart contract’s “recover” function. This incident resulted in a drastic 99% drop in the ELLERIUM (ELM) token’s price within the game.
This article comprehensively explores some of the security challenges faced by Web3 gaming and provides some practical solutions for managing them.
On-Chain and Off-Chain Security Vulnerabilities
Security issues in Web3 gaming can be categorized into on-chain and off-chain. Let’s delve into these categories to understand their significance.
On-Chain Vulnerabilities
These are security weaknesses found in a blockchain’s codebase that powers the game, including its smart contracts. They create opportunities for malicious individuals to gain unauthorized access, tamper with data, disrupt transactions, or even harm the entire blockchain network’s operation.
These vulnerabilities can result in various types of attacks, including disrupting the network’s agreement processes, tampering with smart contract functionality, or stealing digital assets.
Let’s now take a closer look at potential on-chain issues in Web3 gaming projects:
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts are often prime targets for potential attacks in cryptocurrency and blockchain projects because they are open-source. The reliability of a smart contract depends on the skills and attentiveness of the developer who creates it. Therefore, mistakes like coding errors, incorrect logic, flawed designs, or developer oversights can lead to issues in a contract’s design.
Some of the most common smart contract vulnerabilities in Web3 gaming include reentrancy attacks, private key theft, front-running attacks, scams involving NFTs, unchecked external calls, and the introduction of malicious code, among others. These vulnerabilities can jeopardize the security and trustworthiness of Web3 gaming platforms.
Reentrancy attacks have been present in Solidity, the popular smart contract programming language, since its early days. These attacks occur when a smart contract allows other contracts to call it, often involving Ether transfers via the fallback function, even before the original call finishes processing.
For instance, the theft of $620 million from the Ronin Network, hosting Axie Infinity, occurred due to a combination of vulnerabilities, including reentrancy and batchOverflow issues.
Vulnerabilities in DAO Governance
In blockchain-based systems like Web3 games, DAO systems are used for governance—that is, making decisions and changes to any aspect of the project’s operations in a decentralized manner. However, these governance systems can be manipulated through deliberate efforts or by collusion among participants..
This vulnerability remains unless they are carefully designed to prevent a single entity from gaining too much power, usually by amassing lots of governance tokens.
For example, an attacker managed to steal $182 million from Beanstalk protocol by tampering with governance, which typically begins with accumulating a substantial number of the DAO’s governance tokens.
Cross-Chain Vulnerabilities
Web3 gaming projects have moved beyond just Ethereum and BNB, and developers are now exploring alternatives like Optimism, Avalanche, Solana, and Arbitrum. They are doing this to become more competitive and to find cost-effective and efficient solutions. However, security issues can arise when transferring assets between different blockchains.
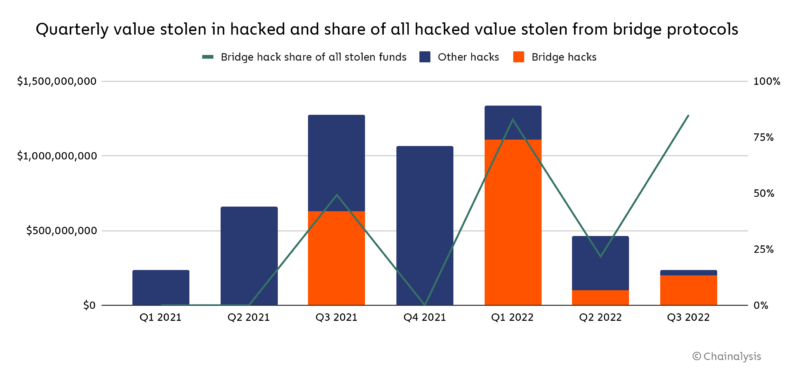
The issue with blockchain bridging is that attackers can tamper with transactions if proper validation and authentication mechanisms are not in place. This can grant them unauthorized access to assets on the other chain. For example, a malicious actor could manipulate transaction data or signatures in a cross-chain transaction, gaining assets on the other blockchain without approval.
According to Chainalysis, 69% of the funds stolen from cryptocurrency projects in 2022 came from cross-chain bridge breaches. Cross-chain bridges are attractive targets because they often hold large sums of funds, either in smart contracts or centralized platforms.
Off-Chain Vulnerabilities
Off-chain vulnerabilities in Web3 gaming involve various potential security threats that can affect blockchain applications from external sources—that is, agents that go beyond the blockchain’s core structure. These vulnerabilities are significant because they can undermine the secure functioning of Web3 gaming projects. Let’s explore a few of them:
Oracle Vulnerabilities
In Web3 gaming, oracles are used to get real-world data for smart contracts. They link off-chain data to on-chain contracts. But if they aren’t properly secured, hackers can manipulate or compromise them, causing wrong data that can harm in-game dynamics or financial transactions.
Economic Manipulation
In Web3 gaming, concerns have been rising about economic manipulation tactics. These issues go beyond the blockchain and can disrupt in-game economies, affecting the player experience and the value of digital assets.
Dependence on Centralized Servers
Web3 gaming projects rely on centralized servers for off-chain components, including backend logic, user interfaces (UI), and backend APIs. These off-chain elements introduce a vulnerability factor similar to traditional Web2 projects in the Web3 environment.
For instance, Web3 gaming projects handle numerous in-game items, and utilizing decentralized storage solutions like IPFS might prove cost-prohibitive. Consequently, the data linked to the game’s NFTs is often stored as JSON on a centralized storage platform. This dependence on centralized storage opens up the possibility of tampering with NFT data if the storage platform lacks adequate security.
Social Engineering Scams
One common but often missed security issue in the blockchain world, especially in Web3 gaming, is fraud. The project’s own developers sometimes organize these social engineering scams. The Squid Game scam is a widely recognized example of this.
The game developers leveraged the popularity of a TV series with the same name and deceived the unsuspecting users into playing games and purchasing items but vanished into thin air with their funds.
Another common tactic is the Ponzi scheme, where early investors are paid using funds from newcomers. Some Web3 gaming projects employ these strategies to sustain themselves financially. However, the problem is that someone at the end of this chain will eventually suffer financial losses.
Solutions to Web3 Gaming Security Challenges
There are certain choices Web3 game developers must make to keep their project and its users safe and protect them from being exploited. Let’s look at some of them:
Establish Bug Bounty Programs
Bug bounty programs involve hiring ethical hackers to identify and report security issues in systems or software, contributing to enhanced Web3 gaming security.
These programs provide a safety net, encouraging security researchers and ethical hackers to collaborate with Web3 gaming projects. They help to detect security problems early, facilitate swift resolution, and prevent future security concerns.
Security researchers and ethical hackers are incentivized to meticulously examine the project’s code, smart contracts, and infrastructure through bug bounty programs. They are more likely to invest their time and skills in finding vulnerabilities, knowing they will be rewarded for their efforts.
Furthermore, bug bounty programs offer a cost-effective approach to security testing by engaging external experts instead of maintaining an in-house security team.
Web3 gaming projects that adopt bug bounty programs demonstrate their commitment to security and transparency, enhancing their reputation and building trust among users, investors, and the broader crypto community.
Conduct Thorough Security Audits
Conducting comprehensive security audits is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance with standards, and mitigating cyber threats. This safeguards an organization’s data and reputation. Developers and investors should prioritize rigorous security audits in these critical areas.
One approach is to seek assistance from third-party security firms like Certik, Fireblocks, Slowmist, and Quantstamp or utilize automated security tools. These steps thoroughly scrutinize the project’s code, uncover potential issues, and expose hidden weaknesses. Through diligent security audits, Web3 gaming projects can fortify their security and safeguard the interests of all stakeholders.
Boost Security for Cross-Chain Bridges
Web3 gaming projects should diligently validate and authenticate all incoming and outgoing cross-chain transactions to ensure their authenticity and accuracy. This process entails meticulous verification of transaction source and destination addresses, verification that the outgoing amount aligns with the expected value, and the utilization of signature-based methods to prevent unauthorized transfers.
Adhering to these stringent validation and authentication procedures significantly enhances the overall security of Web3 gaming projects.
Strengthen Access Controls
To protect Web3 gaming projects from unauthorized access to user and contract accounts, Web3 gaming project creators should put strong access controls in place.
They can do this by using Role-Based Access Controls (RBACs), multi-signature (multisig) wallets, or multi-factor authentication (MFA) methods. These measures collectively create formidable barriers against unwelcome intruders and make the project secure.
In Conclusion,
- Web3 gaming is in its nascent stages, and as it evolves, greater awareness of its potential will drive the implementation of improved security measures.
- To effectively address security challenges, learning from previous incidents is invaluable, particularly given the recurring hacks that have negatively impacted the industry.
- In the future, the Web3 gaming space is poised for continued growth, but security must remain a top priority. With a proactive approach and adopting best practices, Web3 gaming can thrive while safeguarding users and investors from exploitation.
Disclaimer: This article is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be considered trading or investment advice. Nothing herein should be construed as financial, legal, or tax advice. Trading or investing in cryptocurrencies carries a considerable risk of financial loss. Always conduct due diligence.
If you would like to read more articles (news reports, market analyses) like this, visit DeFi Planet and follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and CoinMarketCap Community.
“Take control of your crypto portfolio with MARKETS PRO, DeFi Planet’s suite of analytics tools.”





















