Uniswap, the leading decentralized exchange (DEX) based on total value locked (TVL), continues to set itself apart in a highly competitive market through relentless innovation.
With an impressive $3.9 billion locked on the protocol, its most recent advancement, the v4 upgrade, marks a determined step towards providing real-time utility for its users.
This upgrade builds upon the successes of its v3 upgrade, which introduced concentrated liquidity to enhance capital efficiency for liquidity providers.
The Uniswap v4 upgrade introduces new features and enhancements to the protocol that are precisely designed to meet the evolving needs of users and the broader DeFi sector.
In this article, we explore the key elements of the Uniswap v4 upgrade and how it cements Uniswap’s position as a pioneer in the DEX world.
What is Uniswap v4?

Uniswap v4 is the latest iteration of the Uniswap protocol. It introduces new and improved features that outperform previous iterations and improve the user experience for developers, liquidity providers, and end users.
These improvements not only benefit Uniswap users but also contribute to the overall growth and development of the DeFi ecosystem by setting new efficiency and user experience standards.
The Uniswap team announced the Uniswap v4 upgrade on June 13, 2023.
Improved Features in Uniswap v4
Uniswap Version 4 (v4) is a significant upgrade from its earlier versions, especially in how it manages liquidity pools.
Unlike Uniswap v3, which had a one-size-fits-all approach, Uniswap v4 lets liquidity providers tailor their strategies to fit their needs. This upgrade brings in several new features that make the whole system work better and provide a smoother experience compared to v3.
Let’s take a closer look at the key changes in the Uniswap v4 upgrade that make it better than v3.
Hooks
Uniswap v3 integrated an on-chain oracle mechanism to obtain real-time asset data, enriching the Uniswap experience. However, this led to increased costs for users, and liquidity providers (LPs) had less participatory influence.
But Uniswap v4 introduces a concept called “hooks.” These hooks serve as specialized tools that empower LPs to control trade dynamics. With hooks, LPs can influence factors such as fee collection timing and trade mechanisms.
To better understand hooks, think of them as a set of rules governing pre- and post-trade activities that give LPs the freedom to customize their operations. These rules allow for the modification of parameters such as fee allocation, fee collection timing, trade velocity, and more.
In addition to enabling developers to create AMM DEXs platforms, hooks also improve user interactions. Notably, Uniswap v4 allows the use of tokens from a specific pool to pay gas fees, which was not possible in earlier iterations. This dual benefit diversifies transaction management methodologies while optimizing costs.
The scope of possibilities afforded by hooks within Uniswap v4 is expansive and is subject to the ingenuity of developers. However, fundamental hook operation principles are ingrained within the smart contract architecture.
Singleton
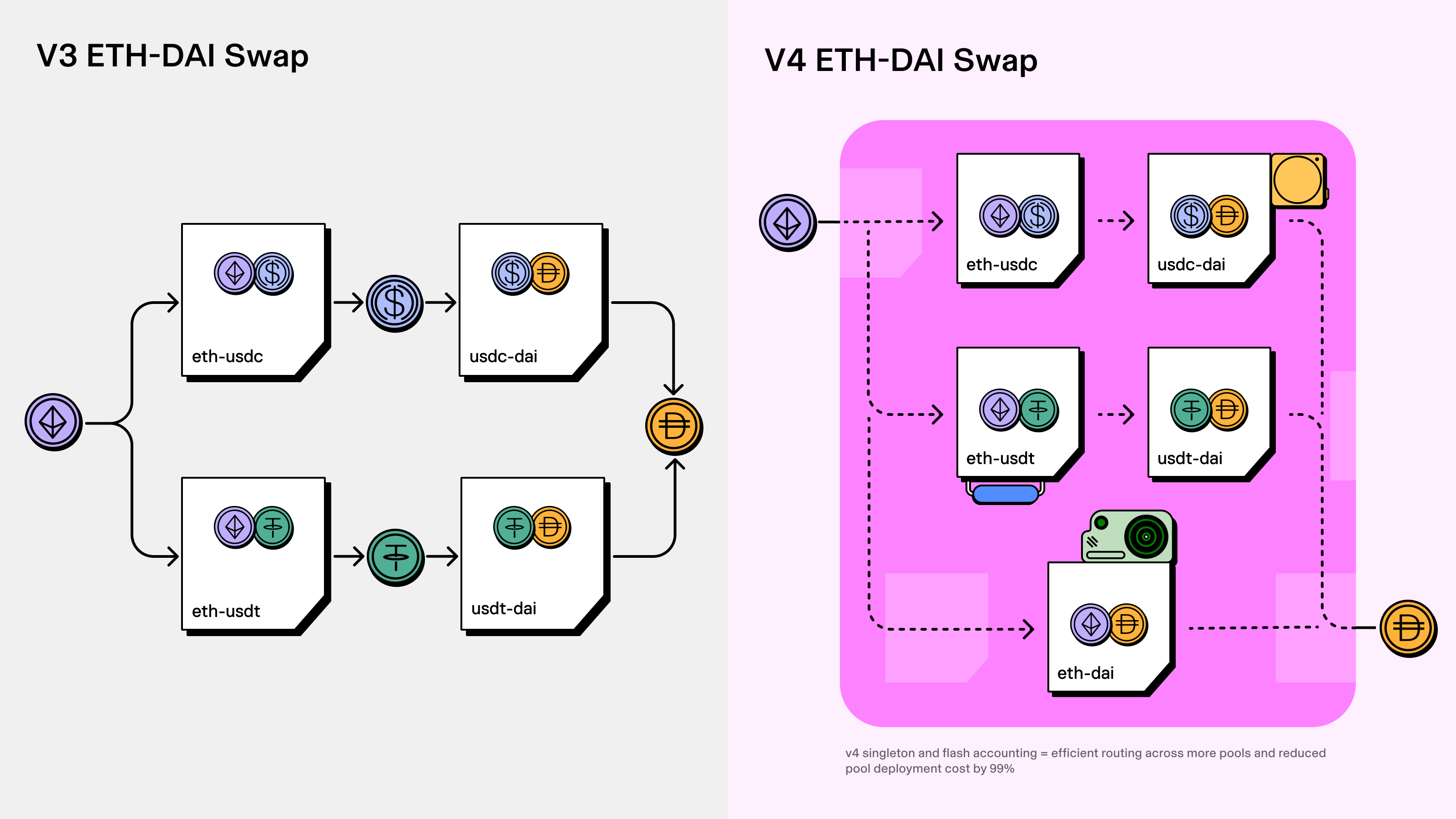
Uniswap v4 introduces the “singleton” feature where a single smart contract oversees all pools in the protocol. This presents an improvement over the v3 model, where each pool deployed on the protocol had its own unique smart contract.
The singleton contract in Uniswap v4 allows for more cost-effective multi-pool swaps compared to Uniswap v3, where pools operate independently with separate rules.
By consolidating pool management into one contract, inter-pool swaps are eliminated, reducing gas fees for pool creation by up to 99%.
For context, consider a hypothetical scenario where you want to swap two tokens: ABC and USDC, and there are two available trading pools on Uniswap v3: ABC/ETH and ETH/USDC. You’d need to interact with both pools to achieve this token swap.
The process involves two steps: first, you swap ABC for ETH, and then you swap ETH for USDC. This dual-step approach increases user fees as each pool charges its individual fee. Also, developers face higher expenses due to the necessity of deploying separate contracts for each of these pools.
In contrast, Uniswap v4 streamlines this process by having a single contract that oversees all pools collectively.
On the other hand, in Uniswap v4, there is a single contract that manages all pools as one entity. Consequently enabling a direct and more cost-effective swap from ABC to USDC compared to the Uniswap v3 model.
Flash Accounting
Flash accounting is a feature of Uniswap v4 that complements the singleton contract. It improves the efficiency of asset swaps by eliminating the need to move assets across pools.
In Uniswap v3, assets were transferred between pools at the end of each swap. This process involved multiple asset movements, resulting in higher costs and gas consumption.
Uniswap v4’s flash accounting system takes a smarter approach – it adjusts net balances instead of moving assets. Only the difference in asset quantities between pools is calculated, avoiding unnecessary transfers. This streamlined approach reduces costs and enhances overall efficiency.
Native ETH Support
Previous Uniswap versions lacked direct ETH support, using wrapped ETH (WETH) for ETH-related swaps. Uniswap v4 now directly supports ETH, allowing users to trade ETH for tokens without WETH. This enhances liquidity, improves ETH-based trading, and aligns with Ethereum’s nature, simplifying DeFi participation.
Governance
Uniswap v4 is governed by the Uniswap community, just like Uniswap v3. Through the UNI DAO, UNI token holders can participate in decision-making processes regarding protocol fees and other management functions.
Uniswap v4 uses a protocol fee mechanism modelled after v3. The UNI DAO can vote to implement a protocol fee for any pool within certain predefined limits.
Uniswap v4 has two types of governance fees: swap and withdrawal. The maximum percentage of swap fees that can be charged for a pool can be set by governance.
If withdrawal fees are enabled, governance can also set the maximum percentage of those fees. However, unlike in v3, fee tiers and tick spacings are not under governance control in v4.
What Does the v4 Upgrade Mean for the Uniswap Protocol?
Uniswap v4 significantly improves the overall experience for developers, liquidity providers, and protocol users. Here are some of the improvements:
Pool customization/Flexibility
Uniswap v4’s hook feature offers a customizable experience, combining multiple functions in a pool. It enables various options, like executing large orders using a time-weighted average market maker, dynamic fees based on volatility, setting on-chain limit orders, and customizable on-chain oracles.
Hooks also control fee settings for swapping and withdrawing liquidity in a pool. This flexibility lets developers customize the Uniswap protocol for their pools or integrations.
All The Reasons To Love The Uniswap V4
Architectural Improvements
Uniswap v4 revamps the protocol’s architecture, especially in pool management. Unlike Uniswap v3, which used separate contracts for each pool, Uniswap v4 employs a single-contract method for multiple pools. This, along with flash accounting, greatly enhances trade efficiency on the platform.
Transaction Fee Reduction
Uniswap v4 upgrade prioritizes lower transaction fees. It employs native ETH, cutting costs by half for ETH to ERC-20 transactions. Pool consolidation and flash accounting further reduce asset transfers, creating a fairer, cost-effective Uniswap protocol.
Challenges of Uniswap v4
While Uniswap v4 undoubtedly introduces a plethora of innovative features, it is not devoid of challenges:
Controversy with the v4 Code’s Format
Uniswap v4’s code adoption introduces a degree of controversy by operating under a Business Source License. This licensing model potentially limits innovation until a transition to a General Purpose License occurs. This transition, scheduled for four years from now, could impact the pace of innovative use cases and solutions. Some developers have already expressed dissatisfaction with the current code format.
Increased Protocol Vulnerability
Uniswap v4’s approach of consolidating all pools into a single contract raises a critical concern due to the vulnerability of smart contracts, which has led to numerous DeFi hacks even after audits. A single exploit in this contract could jeopardize the entire protocol’s safety. The Uniswap team must proactively tackle this challenge by establishing a strong and secure solution to ensure the safety of all pools.
In Conclusion,
Uniswap v4 introduces significant potential for DEX growth with its remarkable features. Its optimization and user-centric design hint at gradual advancements, moving users toward a seamless financial ecosystem.
This progress will reduce friction, enhancing the decentralized marketplace. If concerns are addressed, Uniswap’s future in pushing DEX technology boundaries seems promising.
Disclaimer: This article is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be considered trading or investment advice. Nothing herein should be construed as financial, legal, or tax advice. Trading or investing in cryptocurrencies carries a considerable risk of financial loss. Always conduct due diligence.
If you would like to read more articles like this, visit DeFi Planet and follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and CoinMarketCap Community.
“Take control of your crypto portfolio with MARKETS PRO, DeFi Planet’s suite of analytics tools.”





















