Since the use of DeFi and NFTs has skyrocketed over the past few years, Ethereum has emerged as the primary settlement layer for the crypto-economy. The Ethereum blockchain can only support a certain number of transactions at once. Nonetheless, in this busy environment, users often crowd the Ethereum blockchain as they compete for the limited block space on the network.
As a result of these periods of congestion, users encounter an abysmal user experience, with increased transaction costs and prolonged wait times. The Ethereum community is working hard to solve this problem using both on-chain and off-chain scaling methods.
The long-term scaling strategy of the community is on-chain sharding (or dividing the Ethereum network into numerous “shards”). Builders are increasingly relying on Ethereum-based off-chain scaling options like Layer 2 rollups, which were introduced in 2021. Arbitrum is one such Layer 2 (L2) rollup solution rapidly gaining significant traction.
What is Arbitrum?
Arbitrum is a Layer 2 solution for Ethereum, the world’s largest blockchain for DApps (decentralized applications). It was launched in August 2021 by Offchain Labs. Some of the biggest names in the decentralized finance (DeFi) field, such as Balancer, Curve, AAVE, SushiSwap, UniSwap, and Band Protocol, adopted it almost immediately because it made gas fees cheaper and increased TPS (Transaction Processing Speed).
This Layer 2 solution, which was introduced for Arbitrum smart contracts but was primarily designed for Ethereum, was created to enable the automation of smart contracts on its platform while still depending on the solid security of the Ethereum blockchain. As with any Layer 2 solution, Arbitrum combines multiple smart contracts or transactions into one and uploads them to Ethereum.
The features of Arbitrum include the following:
Ethereum Compatibility
Since Ethereum is the blockchain with the most DApps, ensuring that all developers and cryptocurrency traders can work with DApps on Ethereum is a big advantage.
Trustless Security
Arbitrum is built on Ethereum’s blockchain, one of the most secure blockchains.
Scalability
Arbitrum achieves significantly higher TPS and lower gas fees by removing storage and computation from the Layer 1 blockchain.
Low Cost
Arbitrum can offer users significantly lower transaction costs because it was explicitly designed to reduce gas fees.
What is the Arbitrum Bridge?
The Arbitrum One Bridge allows anyone to send ERC-20 tokens to Arbitrum One, Ethereum’s Layer 2 scaling solution. To use the bridge, you should link your Ethereum wallet to it. You can use any of the supported wallets or MetaMask.
Most of the leading decentralized finance platforms either use Arbitrum or are considering doing so to increase throughput and reduce gas fees. Visit the Arbitrum Layer 2 portal to see a list of all Ethereum DApps it offers.
The “Optimistic” Style of Arbitrum
The two main types of L2 rollups that have emerged to date are ZK (zero-knowledge) rollups and optimistic rollups.
In terms of style, rollups differ due to how they manage data. All rollups perform off-chain transaction processing, which means they use their infrastructure to enable transactions. Rollups help to decongest Ethereum in this regard. In other words, they relieve Ethereum by willingly supporting Ethereum-based transactions that would have otherwise competed for the “L1” Ethereum block space.
Although rollups perform off-chain transactions, these L2s do publish certain information to the Ethereum mainnet.
They are either a ZK rollup or an optimistic rollup, depending on how they perform. The latter relies on “validity proofs.” This includes posting groups of transactions using cryptographic proofs known as “ZK-SNARK.”
Optimistic rollups rely on fraud proofs, which confirm the accuracy of the posted data. Arbitrum’s technology is “optimistic” rather than ZK-based, as it is based on fraud proofs. This approach provides Arbitrum with the following significant advantages:
- L1 dApps can easily “port” their applications to Arbitrum’s L2 technology since optimistic rollups are compatible with the EVM (i.e., Ethereum Virtual Machine).
- Arbitrum benefits structurally from optimistic rollups since they have lower off-chain computation costs and lower fixed-gas fees per transaction batch than ZK rollups.
How Arbitrum Scales Ethereum
Understanding the structure of Arbitrum can help one comprehend how it can offer such low gas fees and fast transaction speeds compared to Ethereum (its L1 blockchain).
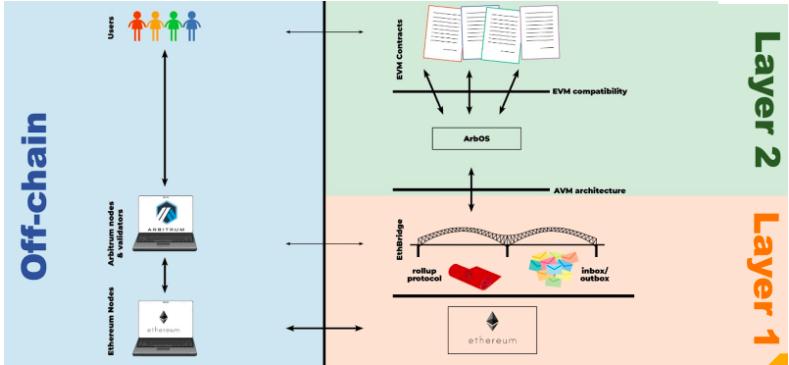
Arbitrum is built with layers that connect and detach it from Ethereum. The scaling solution works as illustrated below:
Arbitrum Layer 1
Layer 1 is the primary blockchain of Ethereum, and it is the bottom layer. This is the source of Arbitrum’s security.
Arbitrum Bridge
The Ethereum-Arbitrum bridge is constructed using a large number of smart contracts. As a result, a link in the Arbitrum chain is formed between Layers 1 and 2, allowing smart contracts to manage the Arbitrum chain automatically.
The Arbitrum bridge, also known as the EthBridge, also arbitrates the Arbitrum rollup protocol, ensuring the efficiency of the layers above it. Arbitrum’s inbox and outbox are also accessible via the Arbitrum bridge, allowing users and contracts to send messages to the chain for processing. The operation of Arbitrum is hugely dependent on this bridge.
AVM (Arbitrum Virtual Machine) Architecture
Although it works with the Arbitrum bridge, this component’s primary function is to distinguish between Layers 1 and 2, ensuring scalability. It ensures that Layer 1 (Ethereum and the Arbitrum bridge) concentrates on the concepts and messages coming from the inbox, execution, and outbox, while Layer 2 (Arbitrum) focuses on executing them. In this approach, Layer 2 makes better use of the computing power than Ethereum, which has lower TPS and higher gas prices.
ArbOS
This software program serves as a controller and a record keeper and runs exclusively on Layer 2. ArbOS ensures that smart contracts work correctly, that records are maintained, and that actions and transactions are done quickly and accurately.
EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) Compatibility
This layer is what enables the widespread use of Arbitrum. Since Ethereum is the platform of choice for DApps and smart contracts, Arbitrum has implemented EVM compatibility to ensure user-friendliness. As a result, developers can create their contracts just as they would on Ethereum, or they can simply port their Ethereum contracts over to Arbitrum to deploy them there at a lower cost and with faster transaction times.
Arbitrum Smart Contracts
Arbitrum smart contracts, or smart contracts deployed by developers on Arbitrum, are at the top of the scaling solution. EVM makes all Arbitrum smart contracts compatible with Ethereum.
The image below (i.e., the Arbitrum network’s infrastructure) is the pictorial illustration of the scaling process.
Steps for Using the Arbitrum Bridge
Step 1: Connect your wallet with the Arbitrum Network
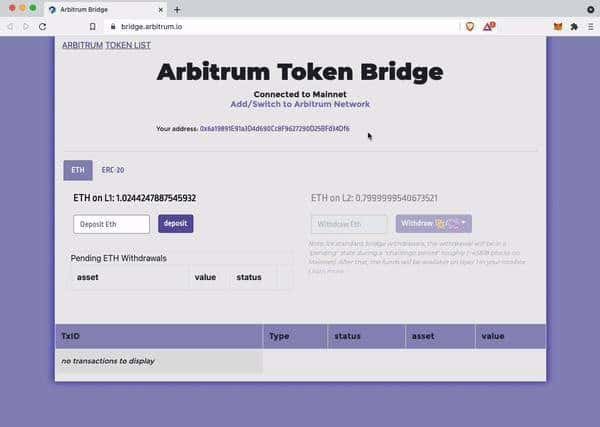
You can add the Arbitrum network to your wallet (for instance, Metamask) by visiting http://bridge.arbitrum.op/ and clicking “Add/Switch to Arbitrum network” in the middle of the page.
Developers can also connect to the Arbitrum One network using Alchemy or Infura.
Step 2: Transfer ETH or ERC-20 tokens from L1 to L2
The Arbitrum One allows users to move Ethereum and other ERC-20 tokens from the L1 network to the L2 network. Bridge your assets from the primary Ethereum network to Arbitrum One before you can use Arbitrum One. You can do this by visiting Arbitrum Bridge.
- Confirm that you are connected to the Ethereum mainnet.
- From the token drop-down menu, choose the token you want to bridge.
- In the “L1” column, enter the amount of ETH or tokens you wish to bridge, and then click “deposit.” To confirm, adhere to the directions on Metamask.
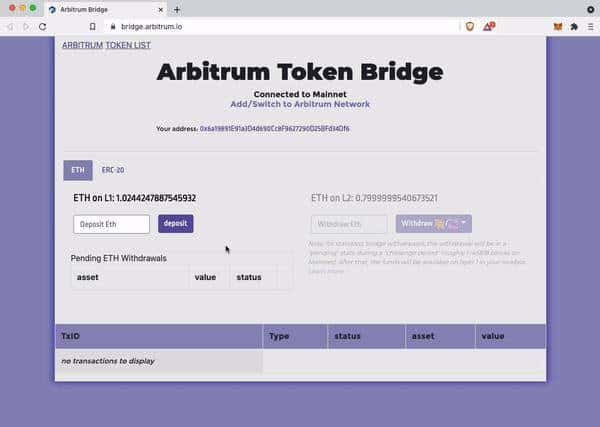
- Depending on how congested the network is, funds will be sent to Arbitrum One Within 10 minutes to 1 hour of submitting a transaction on Metamask.
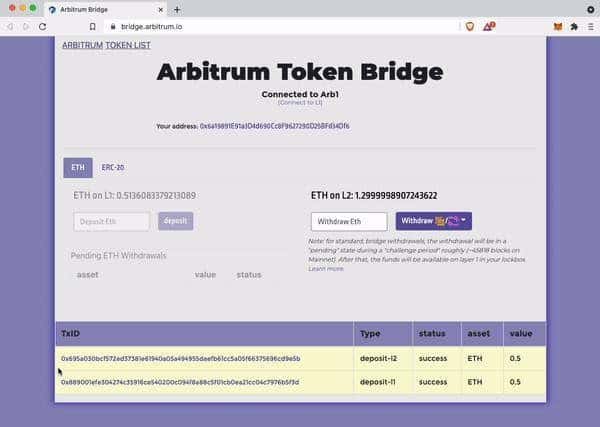
Step 3: Withdraw from Layer 2 (L2) to Layer 1 (L1)
You must set your Metamask wallet to the Arb1 network to withdraw tokens from the Arbitrum L2 network to the L1 network. Then enter the number of tokens you wish to withdraw in the “Withdraw” section.
It will take about a week before you can access your money on the L1 network.
In Conclusion,
- High gas fees shouldn’t hinder you from taking full advantage of Web3. Connecting your assets to L2 networks is an excellent method to sustainably explore the value of Web3.
- As reflected on the Arbitrum One Portal, many dApps are deployed on L2. Simply bridge your ETH and connect your MetaMask wallet to enjoy low gas fees.
- Big players in the cryptocurrency industry have shown interest in the Arbitrum Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum because of its effectiveness and flexibility. Due to its technology’s full compatibility with Ethereum, developers can easily move their DApps over to take advantage of the platform’s faster transaction times and lower gas fees.
- Aside from scalability, the absence of an arbitrum token or coin is also beneficial for Ethereum’s value because the more scalable the system is, the more valuable ETH becomes.
Disclaimer: This article is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be considered trading or investment advice. Nothing herein should be construed as financial, legal, or tax advice. Trading or investing in cryptocurrencies carries a considerable risk of financial loss. Always conduct due diligence.
If you would like to read more articles like this, visit DeFi Planet and follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram.
“Take control of your crypto portfolio with MARKETS PRO, DeFi Planet’s suite of analytics tools.”





















