As the blockchain space continues to expand in 2025, we’re seeing a clear shift toward a multichain future, where users, assets, and applications move fluidly across different networks. In this evolving landscape, one concept keeps coming up: EVM compatibility.
EVM-compatible chains allow developers to build and deploy dApps using the same tools and codebases as they would on Ethereum. This compatibility has become a major driver of growth, enabling faster development, greater interoperability, and broader adoption.
Understanding what Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility means, and why so many chains are embracing it, is key to making sense of today’s fragmented yet interconnected blockchain world. Whether you’re a developer, investor, or user, knowing how EVM-compatible blockchains work can help you spot opportunities and navigate the ecosystem more effectively.
What Is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)?
The EVM is the core technology that powers Ethereum’s ability to run smart contracts. It functions as a decentralized computing environment that executes code exactly as written, across a global network of Ethereum nodes.
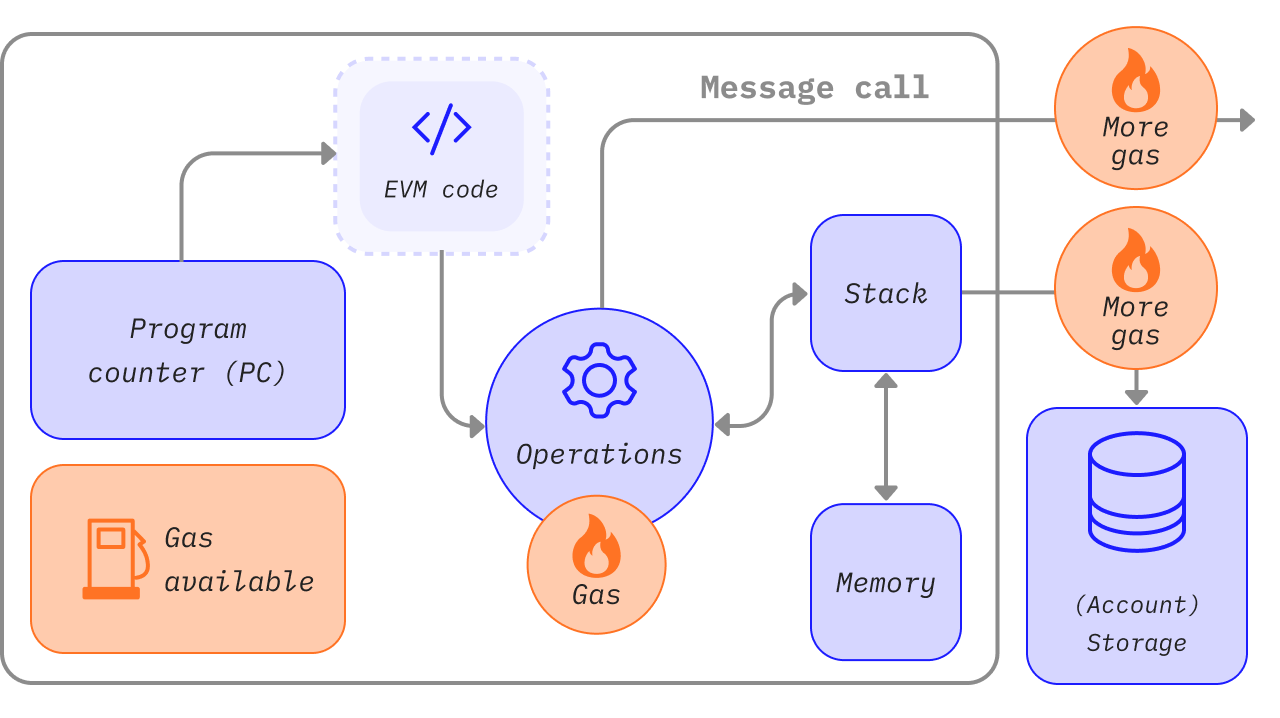
At its core, the EVM acts like a universal processor for the Ethereum blockchain. When a smart contract is deployed or a transaction is triggered, it’s the EVM that interprets and executes the underlying code. Every node in the Ethereum network runs its own instance of the EVM, ensuring all transactions are verified and agreed upon in a trustless and deterministic way.
The Ethereum Virtual Machine is critical to Ethereum’s functionality because it enables the platform to go beyond simple peer-to-peer transfers. It allows developers to create complex applications, ranging from DeFi platforms to NFT marketplaces, using programmable, self-executing contracts.
Think of the EVM as the engine behind all Ethereum-based dApps. It provides the rules and environment in which contracts are securely executed, regardless of the hardware or location of the node running them. Without the EVM, Ethereum would be just another cryptocurrency. With it, Ethereum becomes a programmable blockchain capable of supporting a vast and growing ecosystem of decentralized applications.
What Makes a Blockchain EVM-Compatible?
A blockchain is considered EVM-compatible when it can interpret and execute Ethereum Virtual Machine bytecode, the low-level machine code that the Ethereum Virtual Machine understands.
This means smart contracts compiled for Ethereum can run on these chains without needing to be rewritten. EVM-compatible chains replicate the core logic of Ethereum’s virtual machine so that contract behaviour remains consistent across networks.
Support for Solidity and Ethereum-Based Developer Tools
Beyond bytecode compatibility, EVM-compatible blockchains support Solidity, Ethereum’s primary smart contract programming language. They also integrate with familiar Ethereum development tools like Remix, Hardhat, Truffle, MetaMask, and Web3.js.
This makes it easy for developers to build, test, and deploy dApps using the same workflows they already know, without learning a new programming language or environment.
Examples of EVM-Compatible Chains
Several prominent blockchains have adopted EVM compatibility to attract developers and users from the Ethereum ecosystem. These include:
- BNB Smart Chain (BSC) – Offers faster block times and lower fees while supporting Ethereum-compatible smart contracts.
- Avalanche C-Chain – A component of Avalanche’s multi-chain architecture designed specifically to run Ethereum-compatible dApps.
- Polygon – A Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that supports Ethereum Virtual Machine-compatible smart contracts with faster and cheaper transactions.
- Optimism and Arbitrum – Leading Ethereum Layer 2 rollups that execute smart contracts off-chain and post the results to Ethereum, all while maintaining full EVM compatibility.
These chains lower the entry barrier for developers and foster cross-chain interoperability by maintaining a shared programming standard centered around the EVM.
Benefits of EVM Compatibility
In a rapidly expanding multichain ecosystem, Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility offers powerful advantages for developers, users, and blockchain networks alike:

Cross-Chain Interoperability
EVM compatibility enables dApps to operate across multiple blockchains with minimal changes to their code. This fosters cross-chain interoperability, where assets and smart contracts can interact seamlessly across networks like Ethereum, Polygon, and Avalanche. It also makes it easier for developers to build apps that work with bridges and Layer 2 solutions, expanding their reach while maintaining Ethereum-level logic.
Reduced Development Time and Cost
Because EVM-compatible chains support Solidity and Ethereum tooling, developers can reuse existing code, frameworks, and deployment processes.
This significantly reduces development time and costs, eliminating the need to learn new programming languages or build from scratch when launching on a new chain.
Larger Developer Ecosystem and Community Support
Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility connects developers to Ethereum’s massive open-source ecosystem. This means greater access to community knowledge, pre-built libraries, templates, and documentation.
Developers can find solutions faster, collaborate more easily, and tap into a large pool of contributors, accelerating innovation and reducing friction in the development lifecycle.
Easier dApp Migration and Scaling
For projects looking to scale or avoid Ethereum’s congestion and high gas fees, EVM-compatible chains offer a straightforward path. Developers can migrate their dApps to faster or cheaper networks like Arbitrum or BNB Smart Chain without rebuilding core logic.
This makes EVM compatibility a key enabler of scalability, flexibility, and resilience in today’s multichain environment.
Challenges and Limitations
While Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility has unlocked immense growth and interoperability across blockchains, it also comes with trade-offs. These challenges range from technical limitations to ecosystem-wide consequences that developers and users must consider when building or interacting with EVM-compatible networks.

Security Risks and Smart Contract Portability Issues
Porting smart contracts from Ethereum to other EVM-compatible chains isn’t always seamless. Differences in consensus mechanisms, block times, or fee structures can introduce unexpected bugs or vulnerabilities. A contract that is secure on Ethereum might behave unpredictably on another chain if not carefully audited in its new environment.
Congestion and Performance Differences Across Chains
EVM compatibility doesn’t guarantee identical performance. Some networks may suffer from congestion, slower finality, or inconsistent gas fee structures depending on their infrastructure. Developers must account for these variances, especially when targeting users across multiple Ethereum Virtual Machine chains.
Potential Fragmentation of User Base and Liquidity
With dApps deployed across several EVM-compatible networks, user activity and liquidity can become fragmented. This splintering makes it harder to build strong network effects, affects DeFi protocols that depend on pooled capital, and complicates governance and community coordination.
Limited Innovation Due to Standardization
While Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility simplifies development, it can also limit innovation. Chains may feel compelled to conform to Ethereum’s design choices, even if alternative architectures might better suit their needs. This focus on compatibility can slow down the adoption of novel virtual machines, programming languages, or execution models.
Increased Attack Surface for Multi-Chain dApps
As dApps expand to more EVM-compatible chains, they must manage multiple deployment environments, increasing their overall attack surface. Each new chain introduces its own risks, whether through different validators, bridges, or infrastructure dependencies, creating more entry points for potential exploits.
Why EVM Compatibility Matters for the Future of Web3
As the Web3 ecosystem evolves, the demand for seamless interaction between blockchains is reshaping how decentralized applications are built, used, and scaled.
EVM compatibility has emerged as a key enabler of this vision, helping unify the fragmented landscape and lower the barriers to mass adoption.
The Push Toward Multichain and Cross-Chain Ecosystems
The future of Web3 is not limited to a single blockchain. Instead, it’s becoming a multichain world, where users interact with multiple networks based on their needs, whether it’s speed, cost-efficiency, privacy, or scalability.
Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility supports this shift by allowing dApps and developers to operate across multiple chains using familiar tools and codebases. This flexibility gives users more choice and resilience while helping developers reach broader audiences.
The Role of EVM Compatibility in Scaling dApp Adoption
For decentralized applications to scale, they must be accessible, fast, and inexpensive to use. EVM-compatible blockchains allow dApps originally built on Ethereum to launch on faster, lower-cost blockchains like Optimism, Arbitrum, or Avalanche C-Chain, without significant redevelopment.
This makes it easier to serve global users, especially in regions where high gas fees are a barrier. EVM compatibility also accelerates time-to-market for developers, boosting innovation and ecosystem growth.
How It Contributes to Broader Blockchain Interoperability
True blockchain interoperability means assets, contracts, and users can move freely across networks. EVM compatibility brings us closer to that reality by providing a common technical standard across chains.
This simplifies integration with bridges, wallets, and tooling, enabling smoother interactions between protocols. As more chains adopt Ethereum Virtual Machine compatibility, they become part of a loosely unified network, helping fulfil the Web3 vision of an open, interconnected, and user-controlled internet.
Final thoughts
EVM-compatible blockchains are at the heart of Web3’s evolution, shaping the next generation of decentralized applications through enhanced accessibility, scalability, and interoperability. By supporting Ethereum’s widely adopted standards, these blockchains empower developers to build and deploy dApps faster, with fewer barriers and broader reach.
This compatibility doesn’t just streamline development; it helps unify an increasingly fragmented ecosystem. As the demand for cross-chain interoperability and user-friendly Web3 experiences grows, Ethereum Virtual Machine-compatible networks will continue to play a vital role in making blockchain applications more practical and accessible for the world.
For developers, this is a call to embrace the multichain future, to think beyond a single network and build with interoperability in mind. For users, it’s an opportunity to explore a richer, more flexible Web3 experience, where switching chains doesn’t mean starting over. The future isn’t just Ethereum, it’s every chain that speaks its language.
Disclaimer: This article is intended solely for informational purposes and should not be considered trading or investment advice. Nothing herein should be construed as financial, legal, or tax advice. Trading or investing in cryptocurrencies carries a considerable risk of financial loss. Always conduct due diligence.
If you would like to read more articles like this, visit DeFi Planet and follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and CoinMarketCap Community.
Take control of your crypto portfolio with MARKETS PRO, DeFi Planet’s suite of analytics tools.”





















